But you can't see it, because x 2 is symmetrical about the yaxis So here is another example using √(x) g(x) = √(−x) This is also called reflection about the yShift to the right by 2 units, vertical translation upwards by 3 units The parent function of the graph is y=x^2 Using the general equation y=af(kxd)c, Where if a >Popular Problems Precalculus Describe the Transformation y=x^24 y = −x2 4 y = x 2 4 The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given y = x2 y = x 2 For a better explanation, assume that y = x2 y = x 2 is f (x) = x2 f ( x) = x 2 and y = −x2 4 y = x 2 4 is g(x) = −x2 4 g ( x) = x 2 4
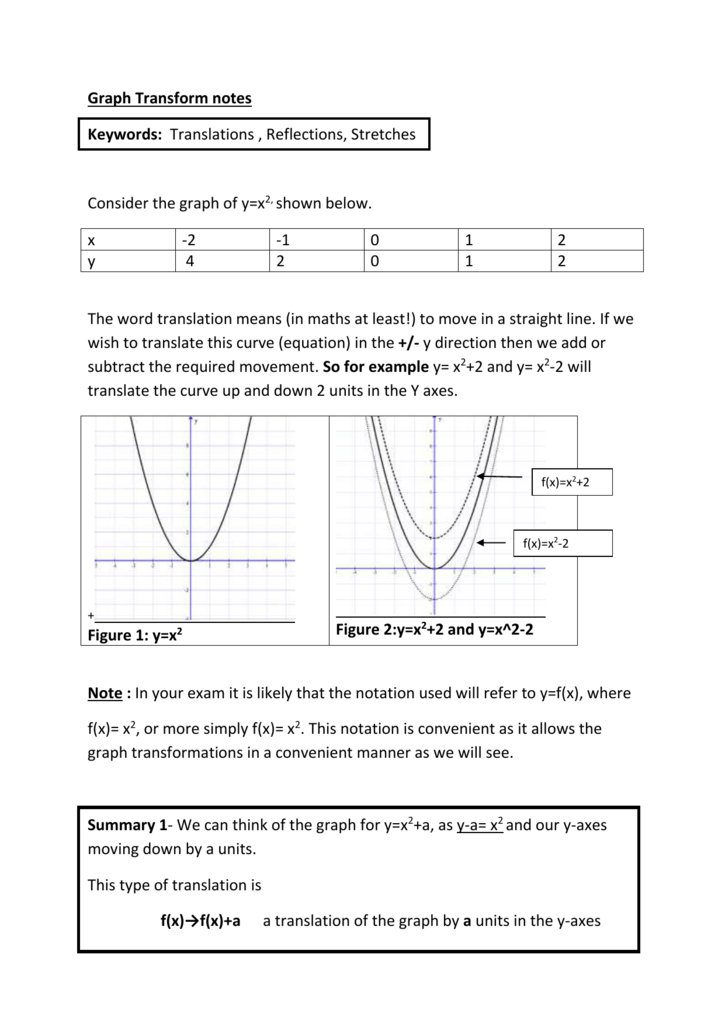
Graph Transform Notes


