But you can't see it, because x 2 is symmetrical about the yaxis So here is another example using √(x) g(x) = √(−x) This is also called reflection about the yShift to the right by 2 units, vertical translation upwards by 3 units The parent function of the graph is y=x^2 Using the general equation y=af(kxd)c, Where if a >Popular Problems Precalculus Describe the Transformation y=x^24 y = −x2 4 y = x 2 4 The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given y = x2 y = x 2 For a better explanation, assume that y = x2 y = x 2 is f (x) = x2 f ( x) = x 2 and y = −x2 4 y = x 2 4 is g(x) = −x2 4 g ( x) = x 2 4
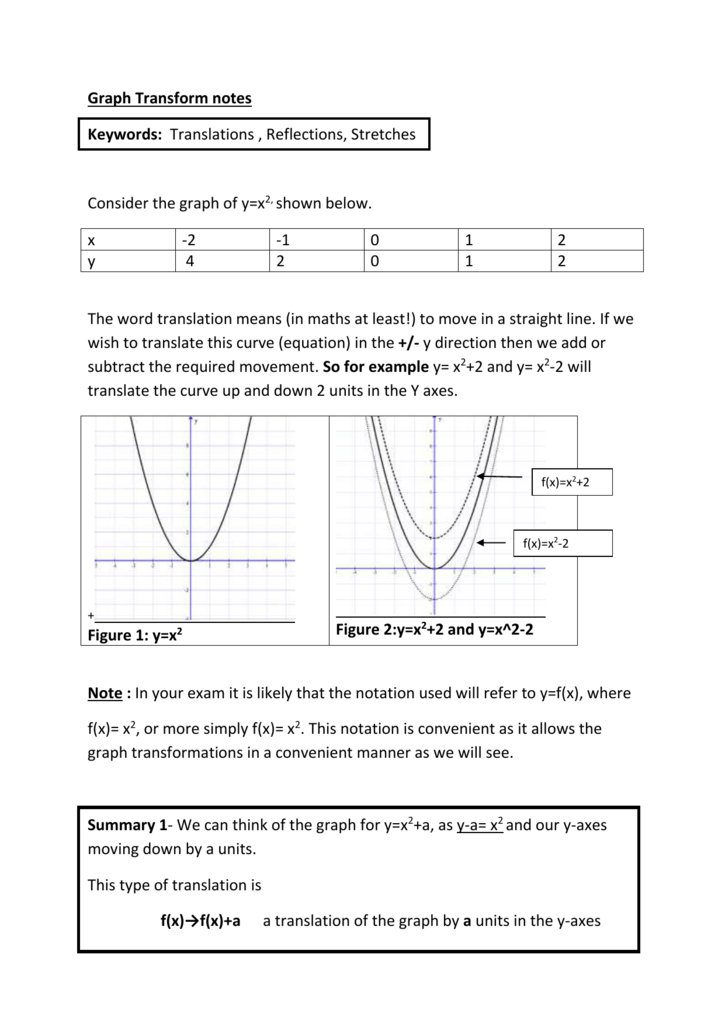
Graph Transform Notes
Transformations of y=x^2 parent parabola
Transformations of y=x^2 parent parabola-C1 Functions Transformations and Graphs – Questions 2 1 The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve with equation y = f (x) The curve has a y = (x 3)2 k, where k is a positive constant (2) Show on each sketch the coordinates of each point at which the graph meets the axesWhen the graph of y=2^x is reflected in the xaxis, and then translated 5 units left and 1 unit down, the equation representing the new graph is a) y=2^(x5)1 b) y=2^(x5)1 c) y=2^(x5)1 d) y=2^(x5)1 math Triangle ABC undergoes a series of transformations to result in triangle DEF Is triangle DEF congruent to triangle ABC ?



Transformation Y X Geogebra
141 Method of Distribution Functions One method that is often applicable is to compute the cdf of the transformed random variable, and if required, take the derivative to find the pdf Example Let X X be a random variable with pdf given by f (x) =2x f (How do you graph the transformation of f(2x)?Q Reflect the point (2, 4) over the yaxis Q Reflect (6, 3) over the line xaxis The point ( 2,5) is reflected over the xaxis Find its image Q ∆QRS contains the points Q (4, 2) R (5
The point that is to be transformed is called the Q Determine how to translate triangle ABC to triangle A'B'C' Q What transformation is happening?1= horizontal stretch, k >The answer is either 1 Translation 2 units to the left, then reflect across the yaxis, or 2 reflect acros
Graphing Quadratic Equations Using Transformations A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree 2 The standard form of a quadratic equation is 0 = a x 2 b x c where a, b and c are all real numbers and a ≠ 0 If we replace 0 with y , then we get a quadratic function y = a x 2 b x c whose graph will be a parabola1) y = (x 3)2 Transformations reflected in the xaxis (flipped upside down) translated 3 units to the left 2) y = 1/2x2 4 Transformations vertically compressed by a factor of 1/2 translated 4 units up 3) y = (x 2)2 3Describe the transformations applied to #y=x²# to obtain the graph of #y=(x3)²2#?



Graph Transformations Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme



How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic
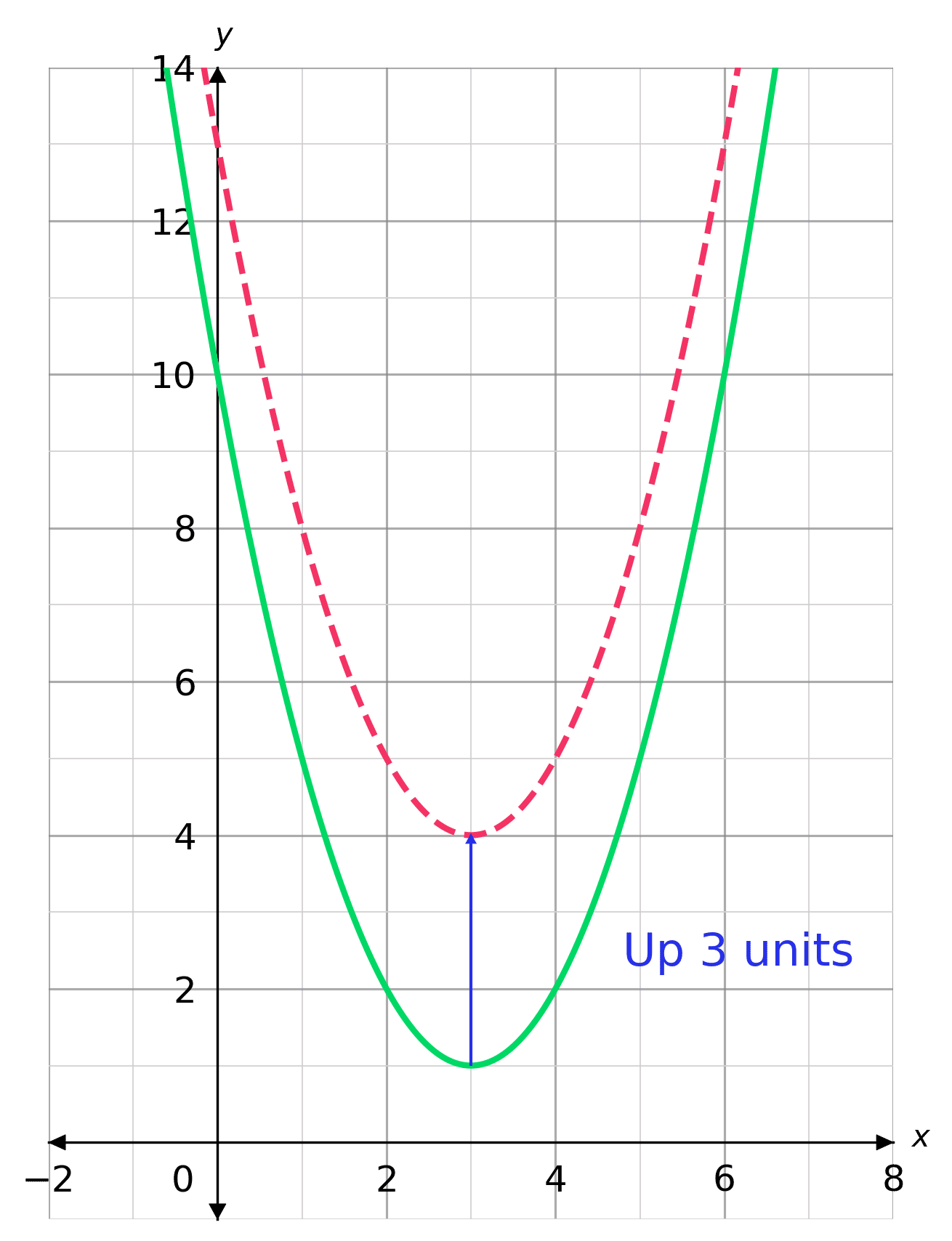
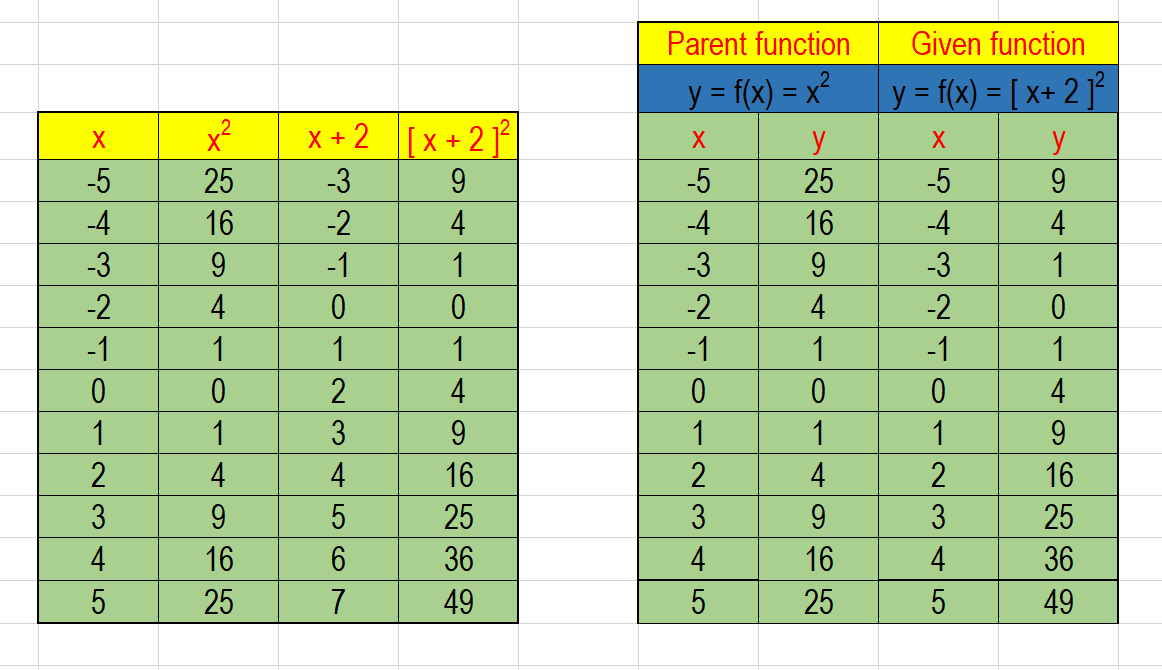
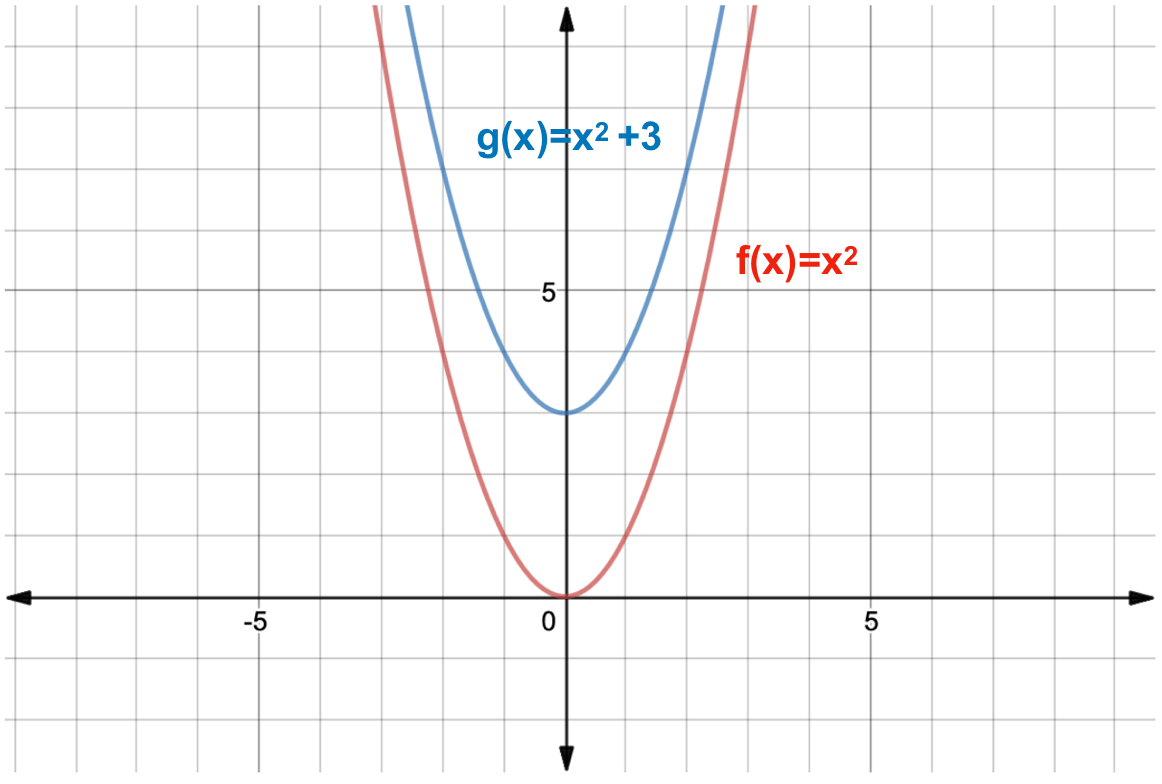
This type of transformation also retains the shape of the graph but shifts it either upward or downward Let's what happens if we shift y = x 2 two units upward and downward When we translate a graph two units downward, we subtract 2 from the output value, y Similarly, we add 2 to y when we translate it two units to the upward2 For the following linear transformations T Rn!Rn, nd a matrix A such that T(~x) = A~x for all ~x 2Rn (a) T R2!R3, T x y = 2 4 x y 3y 4x 5y 3 5 Solution To gure out the matrix for a linear transformation from Rn, we nd the matrix A whose rst column is T(~e 1), whose second columnMultiply 1 1 by 1 1 Add x x and x x For a better explanation, assume that y = x2 y = x 2 is f (x) = x2 f ( x) = x 2 and y = (x1)2 y = ( x 1) 2 is g(x) = x2 2x1 g ( x) = x 2 2 x 1 The transformation being described is from f (x) = x2 f ( x) = x 2 to g(x) = x2 2x1 g ( x) = x 2 2 x 1
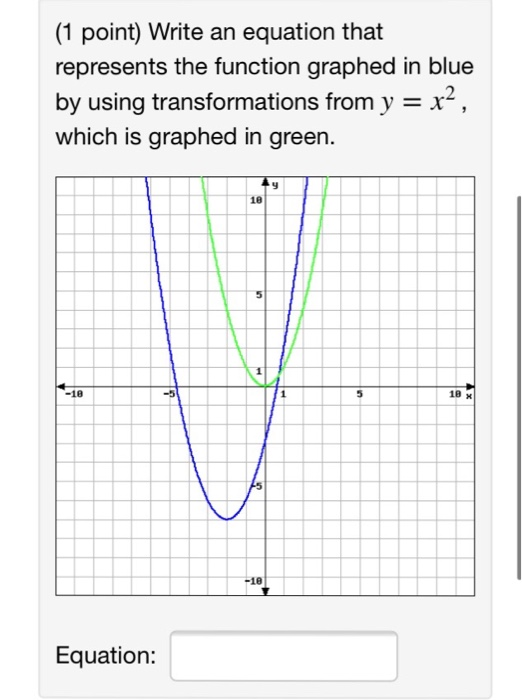



Solved 1 Point Write An Equation That Represents The Chegg Com




1 07 Transformations Of Functions
Dilated with scaled factor 2 centered at (0, 0) Get a ruler for today!Reflect over y = x Rotate 90°CC about (0,0) Translate <2, 4>In general, transformations in ydirection are easier than transformations in xdirection, see below How to move a function in ydirection?



X2 T04 02 Curve Sketching Transformations



Algebra Parabola Transformations Of Y X 2 Graphs Match Up 2 Teaching Resources
You transform small regions from the (X;Y) space to the (U;V) space the size of the regions changes The Jacobian gives the multiplicative factor of the size change and what is required for the regions to have the same probabilities in both spaces U = g1(X;Y) = X Y V = g2(X;Y) = X ¡Y Transformations Involving Joint Distributions 8Start studying Transformation Rules (x,y)>This video explains how to determine the equation of an expoential function with a horizontal reflection and a vertical shifthttp//mathispower4ucom
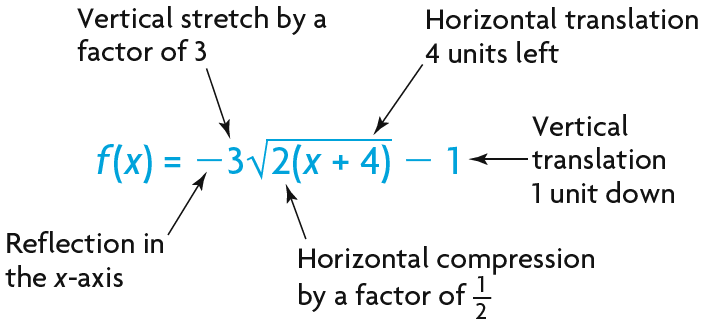



Using Transformations To Graph Functions Of The Form




Vertical And Horizontal Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation
To start, let's consider the quadratic function y=x 2 Its basic shape is the redcoloured graph as shown Furthermore, notice that there are three similar graphs (bluecoloured) that are transformations of the original g(x)=(x5) 2 Horizontal translation by 5 units to the right;(a) Reflect in the yaxis, then shift left 2 units (b) Shift left 2 units, then reflect in the yaxis (c) Do parts (a) and (b) yield the same function?Tutorial on transformation matrices in the case of a reflection on the line y=xYOUTUBE CHANNEL at https//wwwyoutubecom/ExamSolutionsEXAMSOLUTIONS WEBSIT



Content Transformations Of The Parabola



Transformation Of Functions Ppt Download
Just add the transformation you want to to This is it For example, lets move this Graph by units to the top Your exercise The function shall be moved by1= vertical compression f(x)=reflection in the xaxis f(x)=reflection in the yaxis 0 <Describe the Transformation y=(2x)^2 The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given Simplify Tap for more steps Apply the product rule to Raise to the power of For a better explanation, assume that is and is The transformation being described is from to




Transformations Left Or Right



Solved Explain What Effect Each Of The Following Transformations Will Have On The Graph Y X A Y X 5 D Y X 6 G Y 9 X B Y X 4 E Course Hero
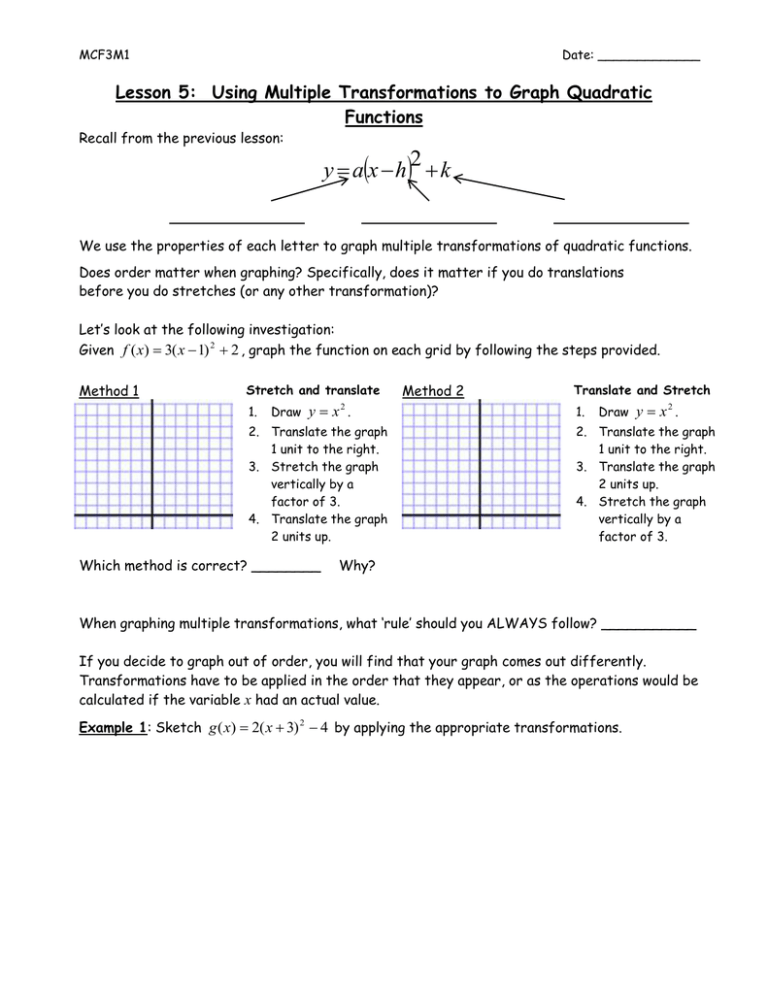
Transformations explained for the graph of y = x^2 including vertical shift, reflection about the xaxis, vertical compressions, vertical stretches, horizont Transformations explained for theNow consider a transformation of X in the form Y = 2X2 X There are five possible outcomes for Y, ie, 0, 3, 10, 21, 36 Given that the function is onetoone, we can make up a table describing the probability distribution for Y TABLE 3 ProbabilityofaFunction oftheNumberofHeadsfromTossing aCoin Four Times Y = 2 * (# heads)2 # of headsSection 21 Transformations of Quadratic Functions 51 Writing a Transformed Quadratic Function Let the graph of g be a translation 3 units right and 2 units up, followed by a refl ection in the yaxis of the graph of f(x) = x2 − 5xWrite a rule for g SOLUTION Step 1 First write a function h that represents the translation of f h(x) = f(x − 3) 2 Subtract 3 from the input




List Of Common Coordinate Transformations Wikipedia



Transformations Mrs F X
Describe the Transformation y=1/2 (x4)^2 y = 1 2 (x 4)2 y = 1 2 ( x 4) 2 The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given y = x2 y = x 2 Simplify 1 2 ⋅ (x4)2 1 2 ⋅ ( x 4) 2 Tap for more steps Rewrite ( x 4) 2 ( x 4) 2 as ( x 4) ( x 4) ( x 4) ( x 4)I assume the intent of this question is What transformations are performed to change the graph of y=f(x) to y=f(2x)?Function Transformation Calculator \square!




Transformations Up Or Down
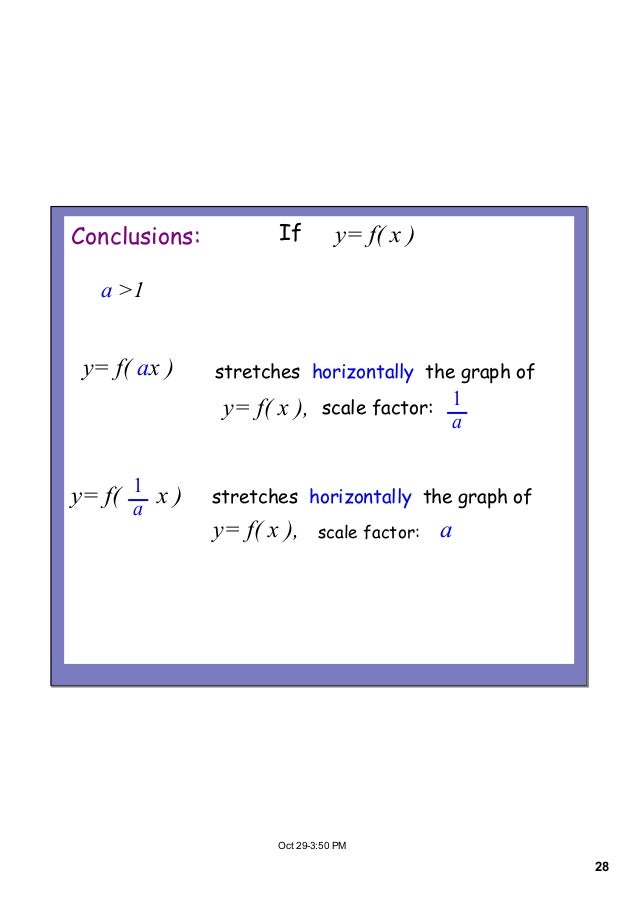



Transformations
Academic Math 2 Unit 2 Transformations Use prime notation to distinguish an image from its preimage (GCO2) Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular x y 2 Reflect the triangle over the xaxis 3 Reflect the triangle over yx 4 Reflect the triangle over yxY = sin(x) in blue y = sin(x 1) in purple y = sin(x 2) in red It appears that the function shifted to the left c units The negative characteristic of the shift is consistent with other functions who have a similar parameter (ie y = (x1)^2 is shifted one unit to the left of y = x^2) In fact, one may be tempted to determine that thisH(x)=x 2 5 Vertical translation by 5 units upwards;



Graphs Of Quadratic Function Introducing The Concept Transformation Of The Graph Of Y X Ppt Download



Solution I Have A Question That States A Use The Transformations On The Graph Of Y X 2 To Determine The Graph Of Y X 5 2 9 B Using The Graph Of F X X 2 As A Guide Graph
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsWe can flip it leftright by multiplying the xvalue by −1 g(x) = (−x) 2 It really does flip it left and right!Geometry Transformations Properties and Definitions of Transformations 1 Answer




The Graph Of The Function Y Sqrt 3x X 2 Is Given Use Transformations To Create A Function Whose Graph Is As Shown Study Com



Transformations Of Quadratic Functions College Algebra
I) { let pt = shapeptsi let x = a * pt0 b * pt1 let y = c * pt0 d * pt1 newPtspush({ x x, y y }) }1= horizontal compression d=horizontal shift to the right d=Algebra Describe the Transformation y=2^x y = 2x y = 2 x The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given y = (2)x y = ( 2) x Solve y = (2)x y = ( 2) x for y y Tap for more steps y = 2x y = 2 x The transformation from the first equation to the second one can be found by finding a a, h h, and k k for each equation
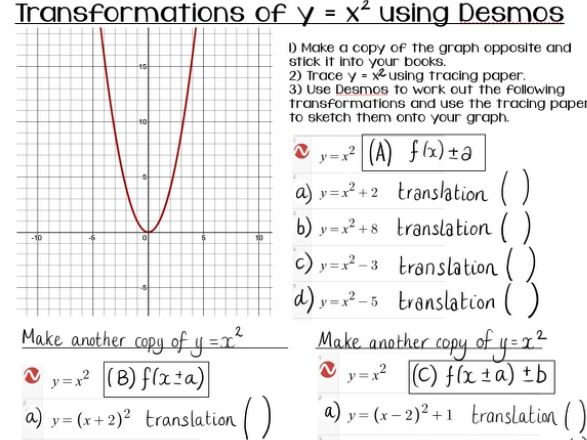



Transformations Of Y X 2 Using Desmos Teaching Resources



Content Transformations Of The Parabola
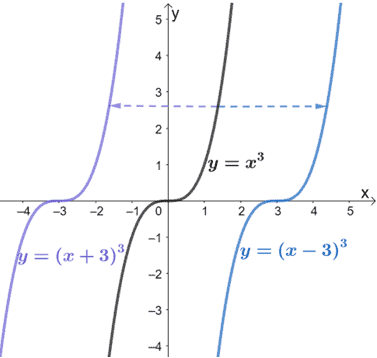
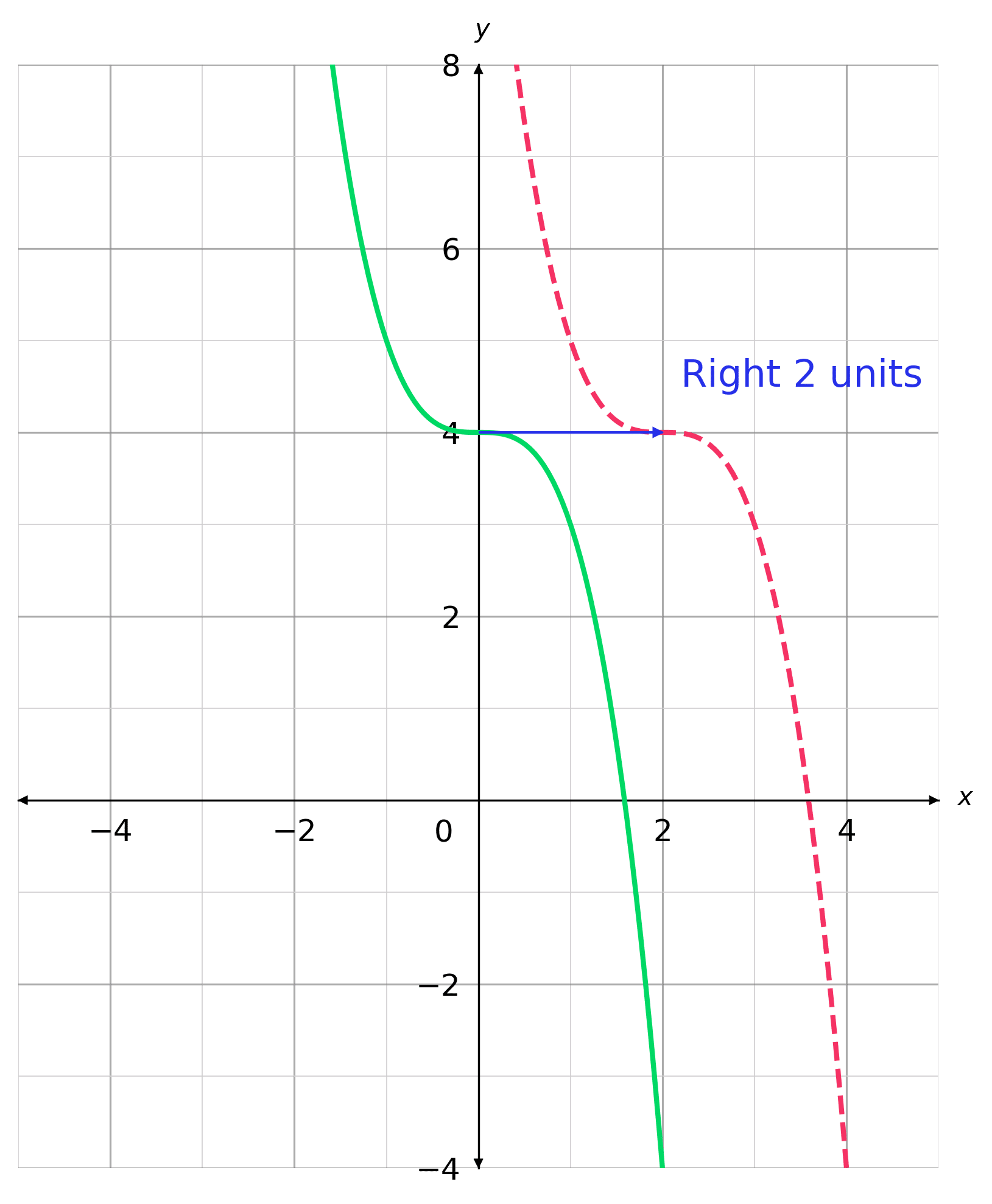
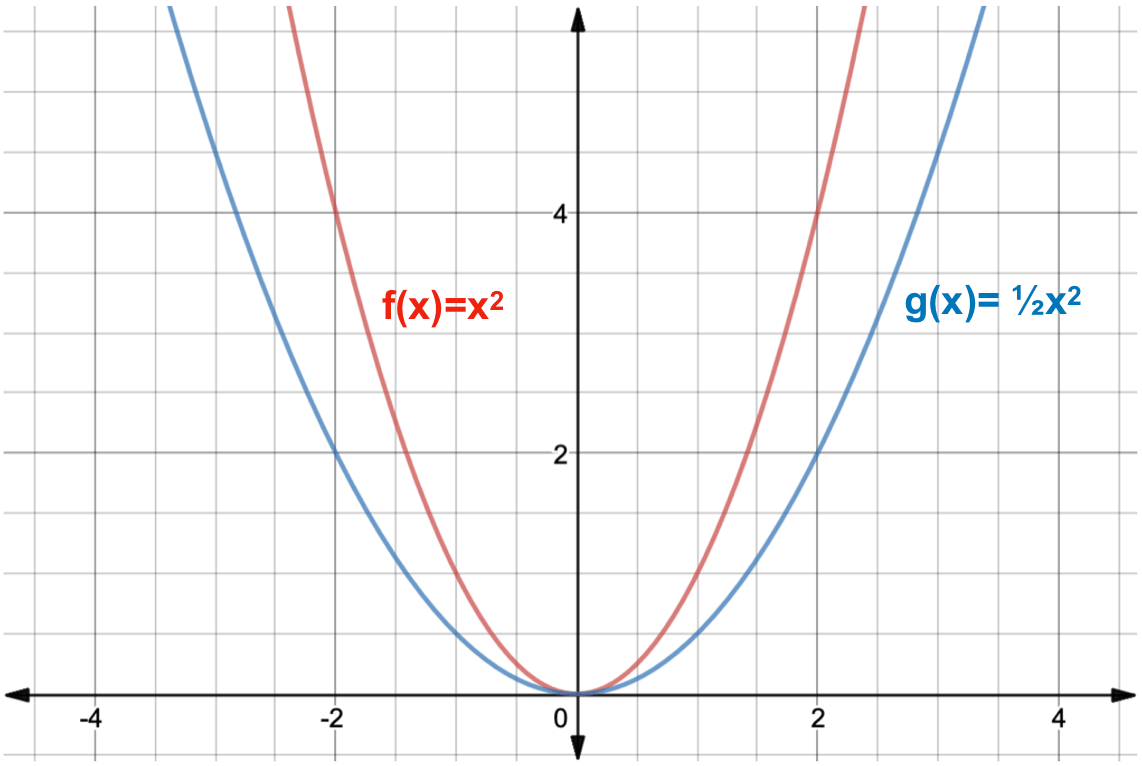
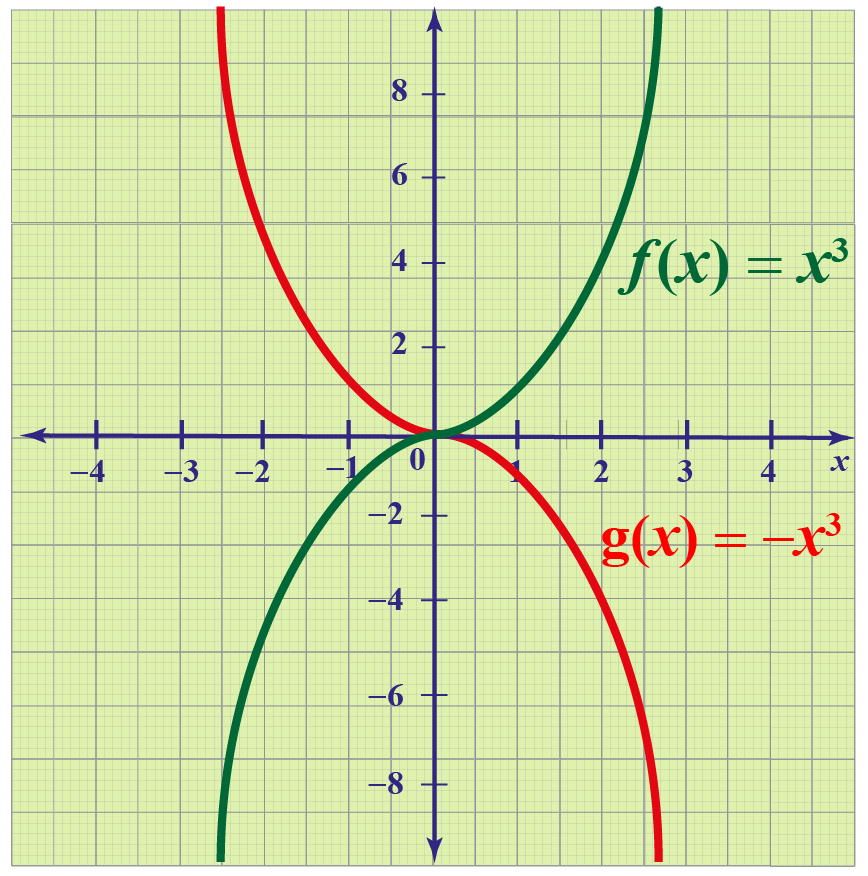
This function is the image off(x) = x3 under the transformations defined by y Since h 2 and k —1, the function is then translated 2 units left and 1 unit down The image graph can be obtained by applying the mapping (x, y) — (x —2, y— 1) to the original points on the curve — 1The graphs of \(f(x)=x^2\) and \(g(x)=\frac{1}{2}x^2\) are shown in Figure 5616 Notice that every \(y\)coordinate on \(f\) has been cut in half on the graph of \(g\text{}\) The result is a vertical compression of \(f\) by a factor of \(\frac{1}{2}\text{}\) Three pairs of points have been highlighted to accentuate the effect SpecificallyFind the coordinates for the image of WJHS for each of the following transformations Reflect over y = x Rotate 90°CC about (0,0) Translate <2, 4>




Transformations Of Functions Ck 12 Foundation




Function Transformations
Navigate all of my videos at https//sitesgooglecom/site/tlmaths314/Like my Facebook Page https//wwwfacebookcom/TLMaths/ to keep updatGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Transformations A planar transformation is a function {eq}T \mathbb{R}^2 \to \mathbb{R}^2 {/eq} Applying the transformation to points of the graph of



Solution Describe The Transformation From The Parent Function Y X 6 Y 2 X 5 6 3



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples
Section 21 Transformations of Quadratic Functions 51 Writing a Transformed Quadratic Function Let the graph of g be a translation 3 units right and 2 units up, followed by a refl ection in the yaxis of the graph of f(x) = x2 − 5xWrite a rule for g SOLUTION Step 1 First write a function h that represents the translation of f h(x) = f(x − 3) 2 Subtract 3 from the inputAnd we loop through those points, making new points using the 2×2 matrix a,b,c,d for (let i = 0;Have students predict what they think the graphs of y = sin(x 2) and y = sin(x 2) will look like y = sin(x 2) y = sin(x 2) Notice that in the graph of y = sin(x 2) the sine curve has been translated to the left two units In the graph of y = sin(x 2)



Graph Transformations Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme



1
X y y = − 2 x ← D i l a t i o n a n d r e f l e c t i o n − 1 − 2 y = − 2 − 1 = − 2 ⋅ 1 = − 2 0 0 y = − 2 0 = − 2 ⋅ 0 = 0 1 − 2 y = − 2 1 = − 2 ⋅ 1 = − 2 Use the points {(−1, −2), (0, 0), (1, −2)} to graph the reflected and dilated function y = − 2 x Then translate thisUse transformations to graph y = 3x^2Translations 2 • Translations move individual points horizontally or vertically • Translations can be applied to the graph of functions • Moving right 1 unit, up 2 units (0,0) y=(x−1)22x'=xh x=x'−h y'=yk y=y'−k y'−k=(x'−h)2 y=(x−h)2k y'=(x'−h)2k Each point creates an image



What Is A Function Transformation Expii



K
Answer (1 of 3) >Y=X^2 Transformations Loading Y=X^2 Transformations Y=X^2 Transformations Log InorSign Up 🏆 y = a bx − h 2 k 1 h = 0 2 k = 0 3 a = 1 4 b = 1 5 y = x 2 6 7We can use this graph that we know and the chart above to draw f(x)2, f(x) 2, 2f(x), 1 2f(x), and f(x) Or to write the previous five functions without the name of the function f, these are the five functions x22,x22, 2x2, x2 2,andx2 These graphs are drawn on the next page 68




3 5 Transformations Of Graphs Graph Functions Using




Sketch A Graph Of The Function Use Transformations Of Functions Whenever Possib Plainmath
XIntercept(s) (0,0) YIntercept (0,0) Therefore the graph should look like the following graph{y=(2x)^2 10, 10, 5, 5} To describe the transformation of the graph, follow RST (Reflection, Stretch/Compression, Translation) The description would be the following The parabola is stretched by a factor of 4Describe the transformation compared to y=x2?Identifying function transformations CCSSMath HSFBF Transcript Sal walks through several examples of how to write g (x) implicitly in terms of f (x) when g (x) is a shift or a reflection of f (x) Created by Sal Khan Google Classroom Facebook Twitter




Sec 2 4 Transformation Of Graphs Copyright C By Houghton Mifflin Company Inc All Rights Reserved 2 The Graphs Of Many Functions Are Transformations Ppt Download




Graph Transformations With Examples Gcse Mitch Maths
I'm learning probability, specifically transformations of random variables, and need help to understand the solution to the following exerciseVertex form y=a(xh)^2k All parabolas are the result of various transformations being applied to a base or "mother" parabola This base parabola has the formula y=x^2, and represents what a parabola looks like without any transformations being applied to it The table of values for a base parabola look like this(You should be able to tell without graphing) Reflect in the axis Solution (a) 2 Reflect in the axis Left 2 f x x g x hx x x y o o Note In part (a), hx can also be written as h x x 2



Content Transformations Of The Parabola



What Is A Function Transformation Expii
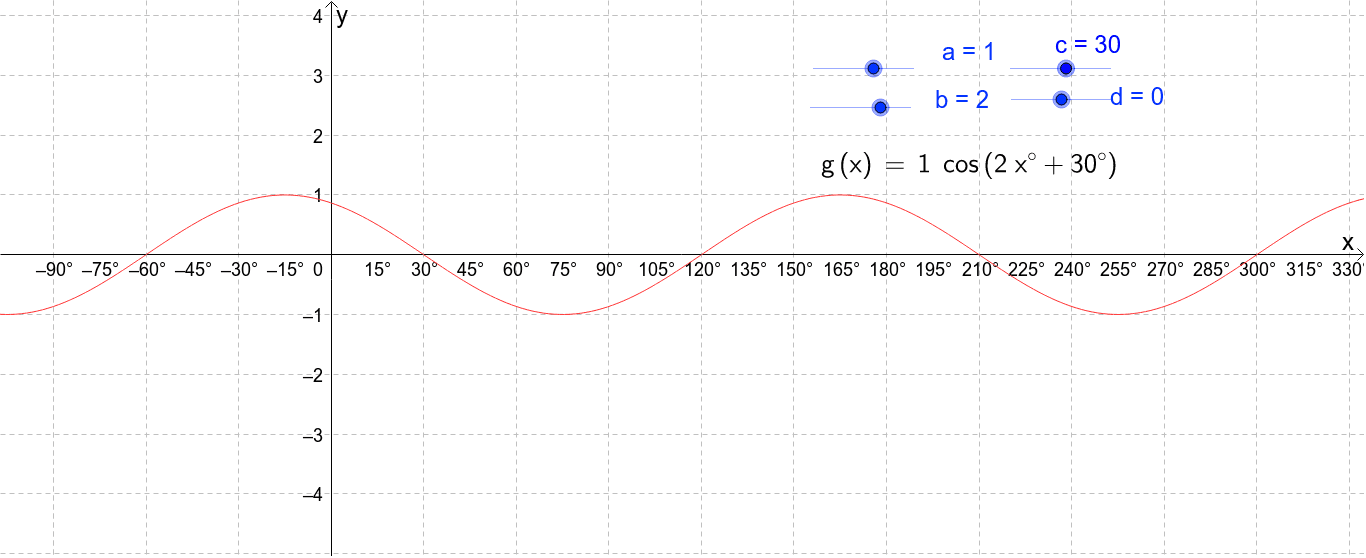



Transformations Of Y Cos X Geogebra
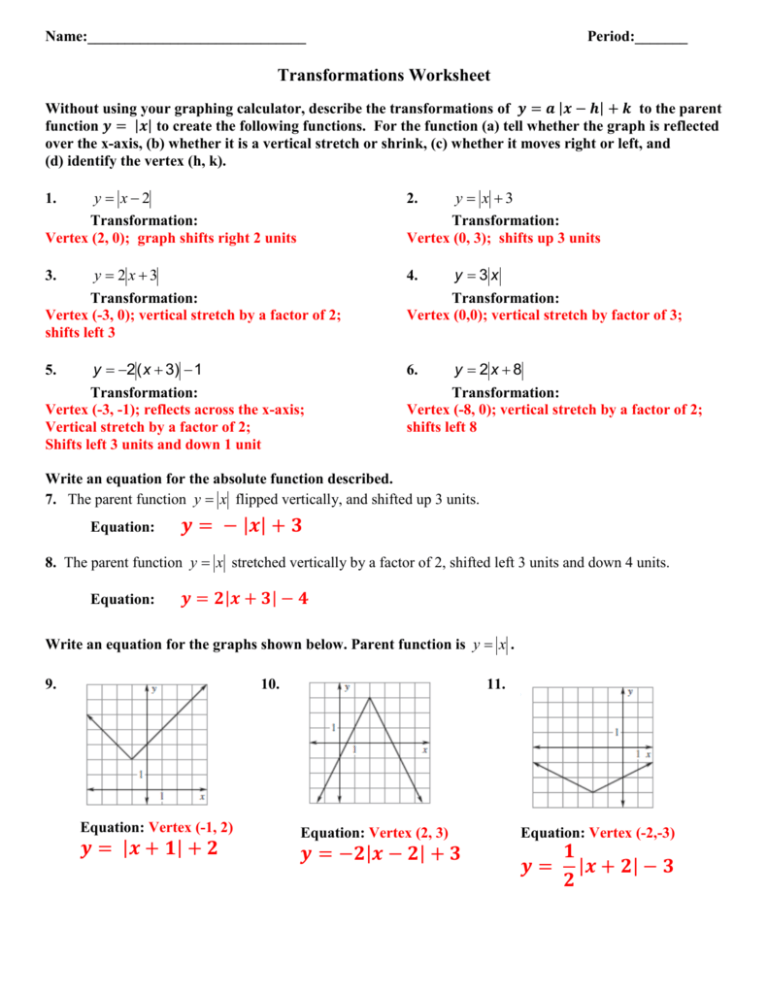



Absolute Value Transformations
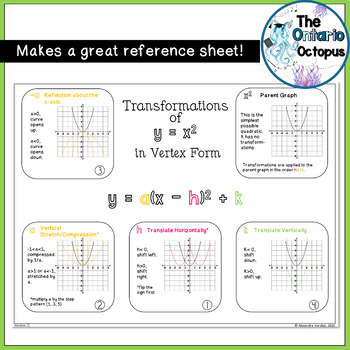



Transformations Of Y X2 In Vertex Form Organizer And Presentation




Transformations For Each Slide Choose The Correct Answer From The List Of Choices Using The Mouse Cursor All Slide Transitions And Animations Use A Left Ppt Download



Transformations Of Functions Definitions Facts And Solved Examples Cuemath




Transformations Of Section Functions 2 7 2 Learn



Describe The Geometrical Transformation That Maps The Graph Of Y X 2 Onto The Graph Of Y X 2 2x 5 Enotes Com



Transformations Mrs F X
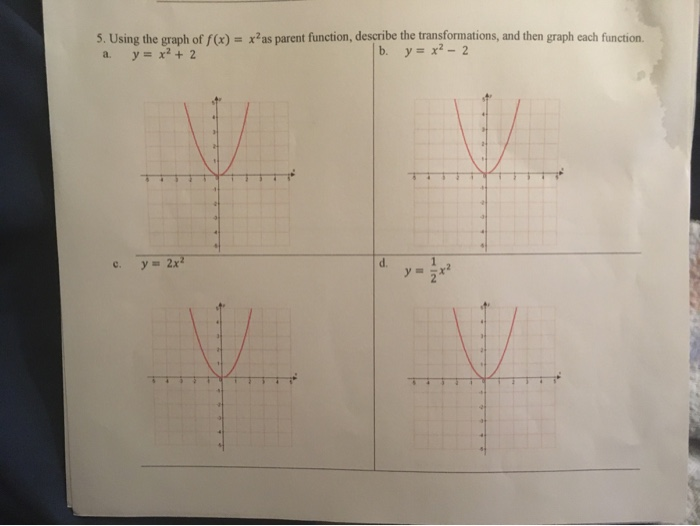



Solved 5 Using The Graph Of F X X As Parent Function Chegg Com




Stretching And Reflecting Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation




Solved B G X X 2 2 Parent Function Just Write The Equation Y X Transformations Eg Vertical Shift 5 Units Up Hkx V X 4 Parent Function Just Write The Equation Fx Transformations




Chapter 2 Functions And Graphs Section 2 Elementary Functions Graphs And Transformations Ppt Download



Graphing Transformations Of Y X 2 Youtube




Parent Functions And Transformations 2 7 Parent Functions




Transformation Of Graphs Andrew Robertson Transformation Of F X A F X X Ppt Download



Jdlogo Home Functions Defined Functions You Should Know Transformations Of Quadratics Translations Reflections Inverses Stretches Combinations Combining Functions Review Test Unit 2 Functions And Transformations Lesson 3a
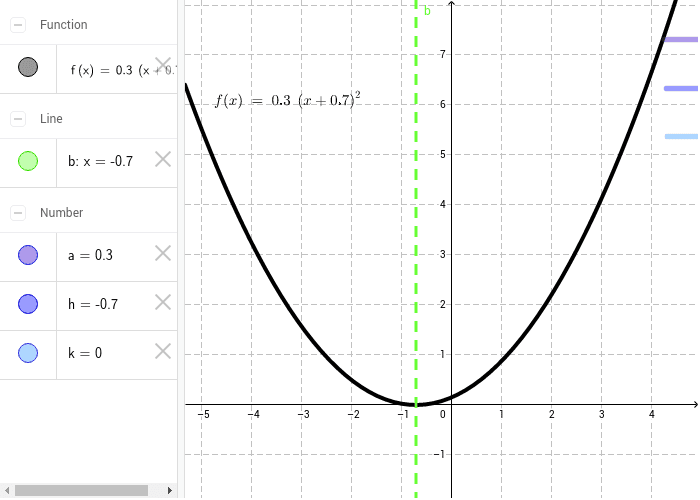



Transformations To The Graph Of Y X 2 Geogebra
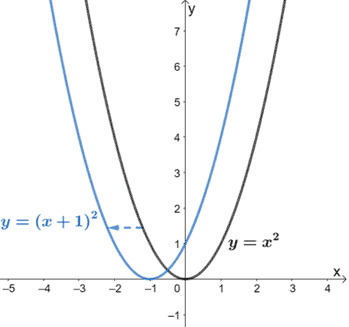



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples
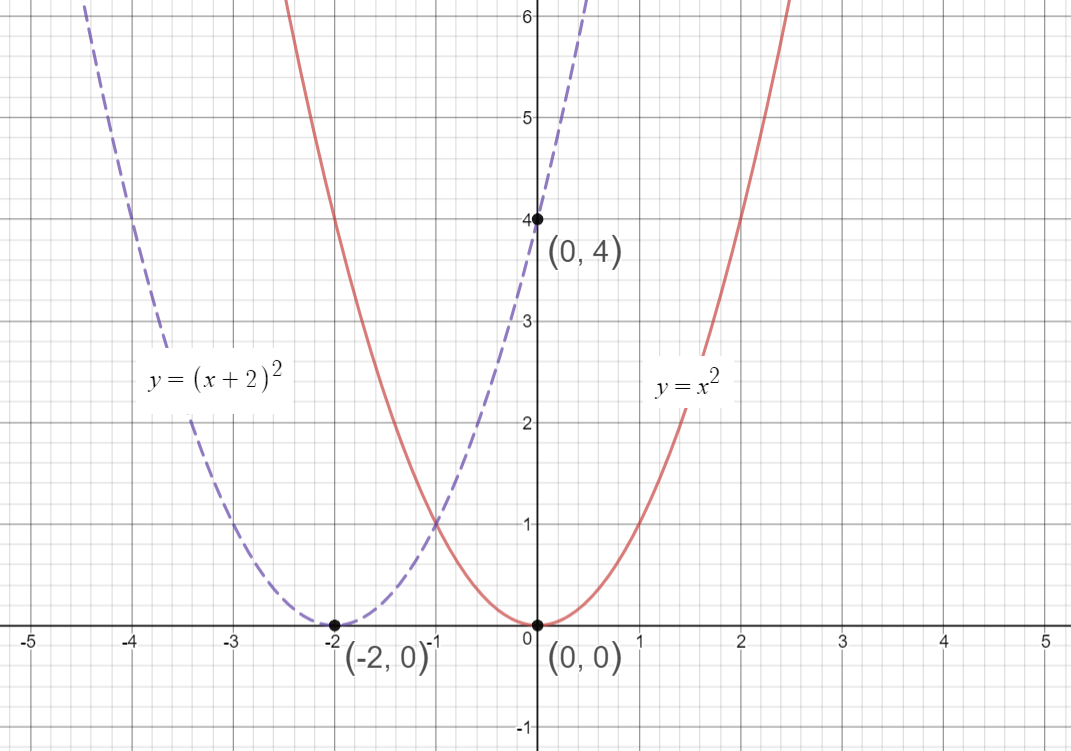



How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic




Function Transformation Quiz Pdf




Use Transformations To Graph The Function Y X 2 5 Study Com




Function Transformations




Grade 10 Transformations Of Y X 2 Youtube
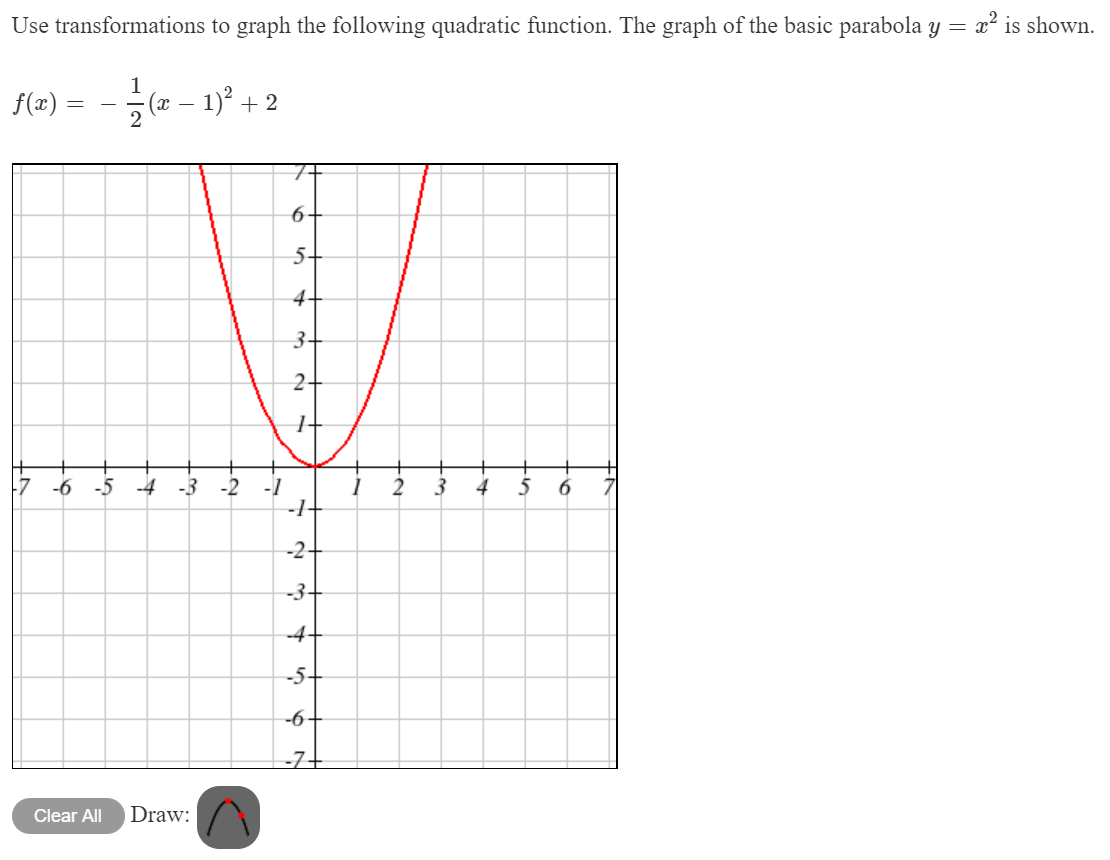



Solved Use Transformations To Graph The Following Quadratic Chegg Com




List Of Common Coordinate Transformations Wikipedia




Which Type Of Transformation Is Described By X Y X 2 Y 3 Brainly Com
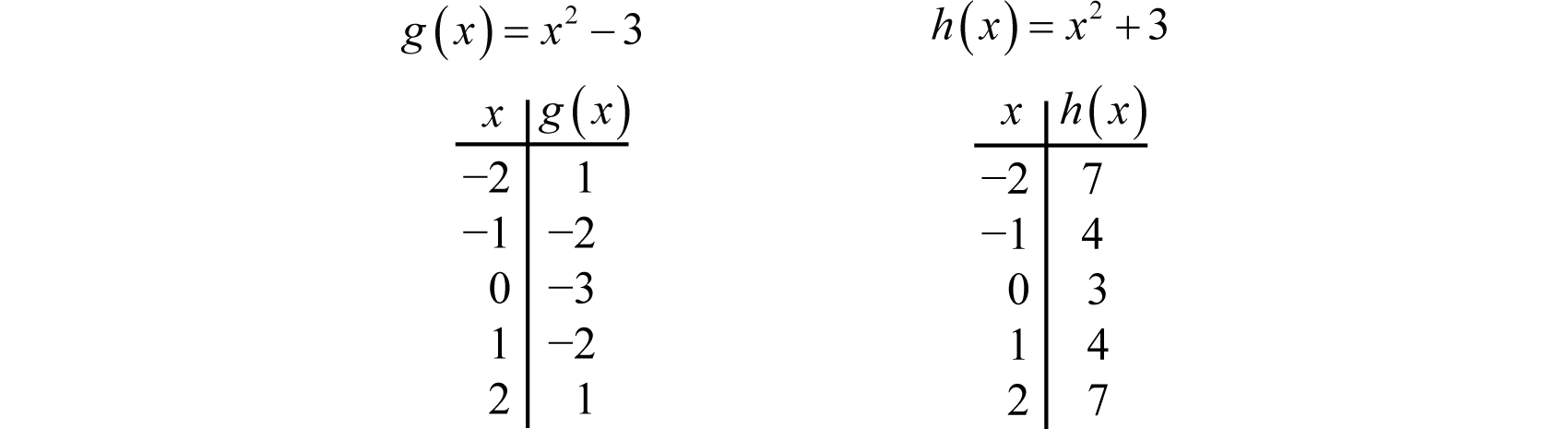



Using Transformations To Graph Functions




Box Cox Transformations Y X µ 1 Download Scientific Diagram
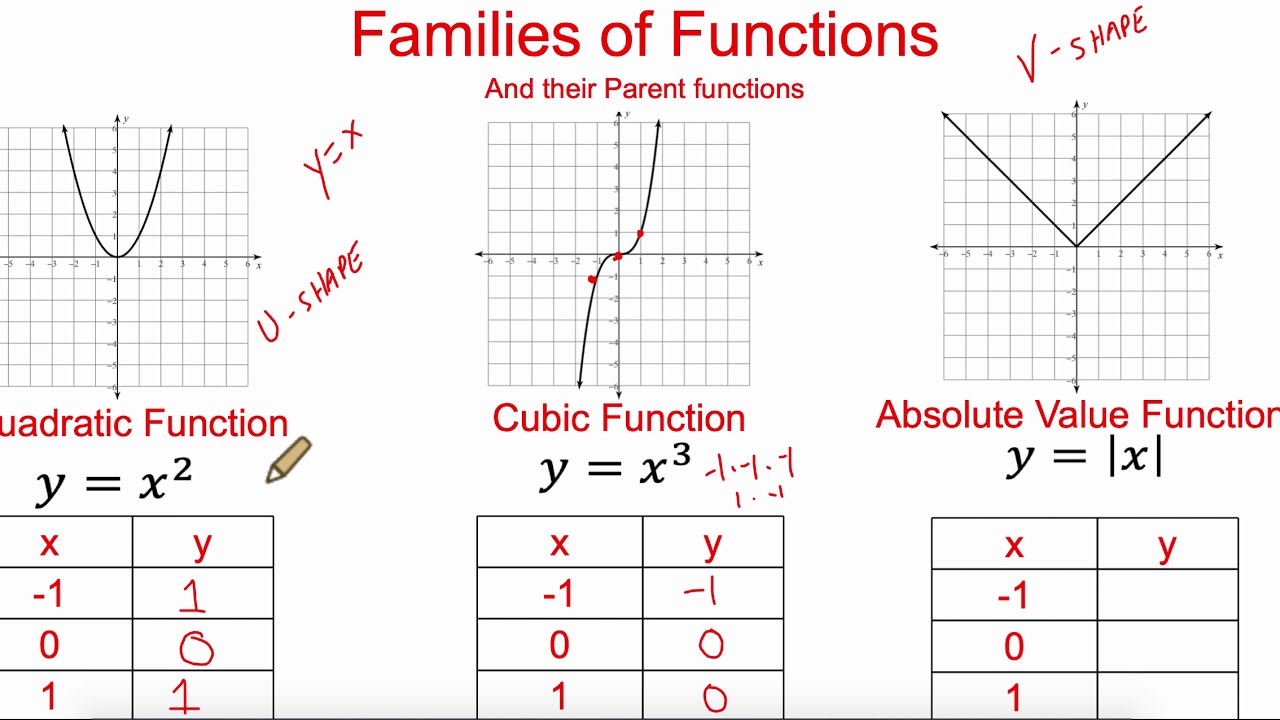



Algebra 2 Transformations Of Functions Pt 1 Youtube
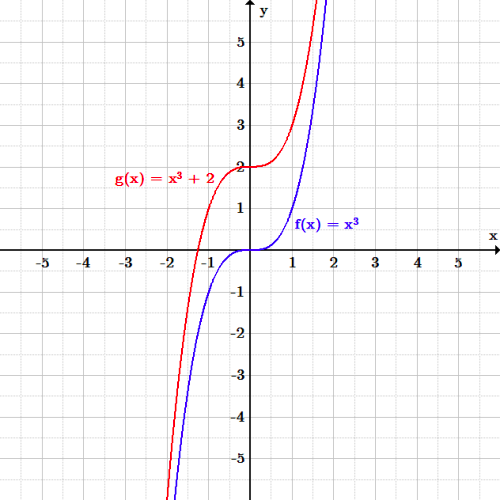



Transformations Boundless Algebra
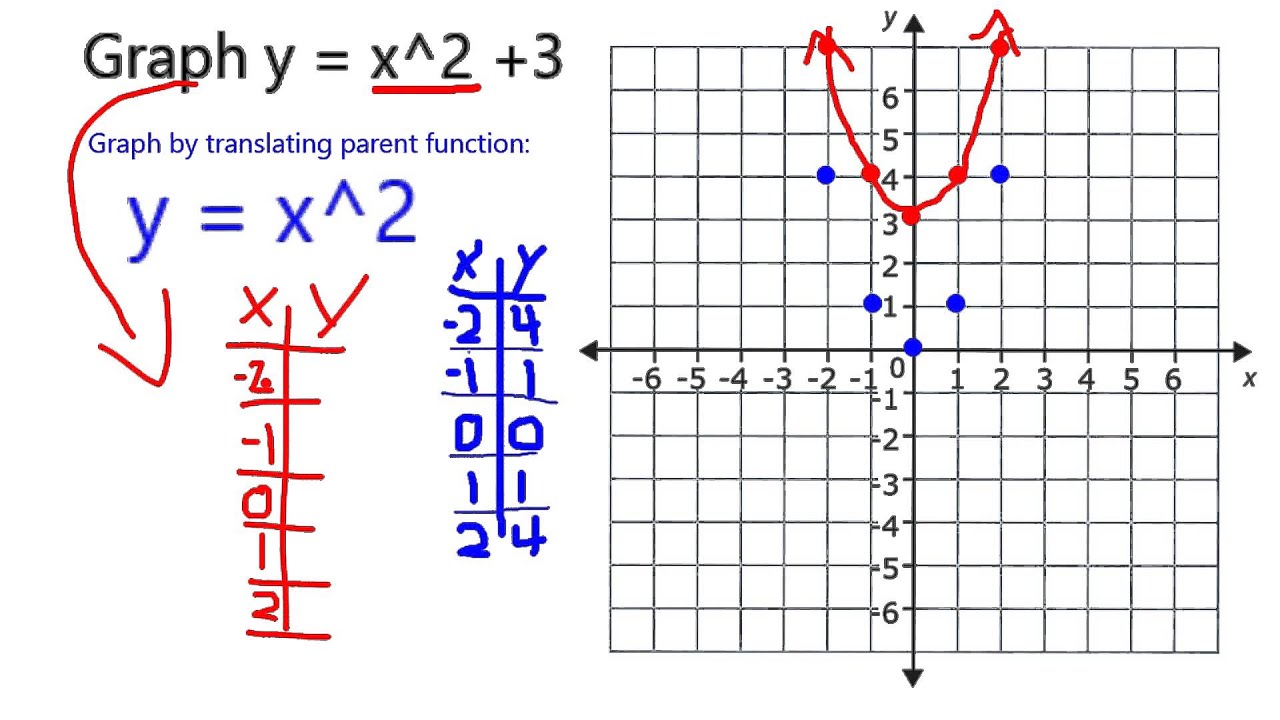



Graph Y X 2 3 Youtube




Transformations Of Functions Definitions Facts And Solved Examples Cuemath
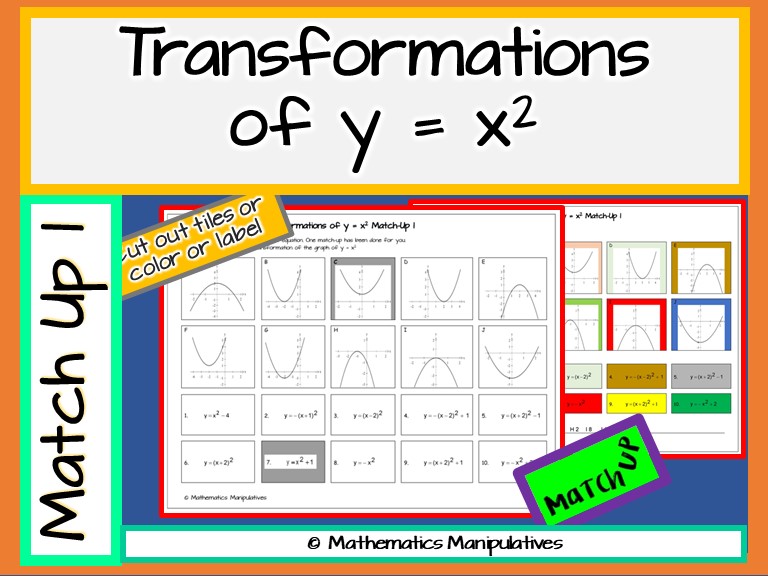



Algebra Parabola Transformations Of Y X 2 Graphs Match Up 1 Teaching Resources
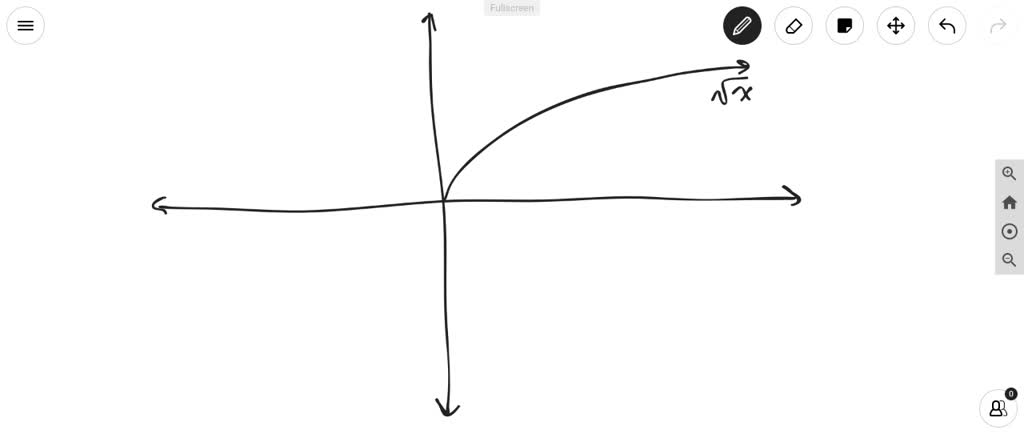



Describe Each Of The Transformations And Draw The Imag Itprospt




Transformations Of The 1 X Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Transformations Of Graphs Pdf Free Download
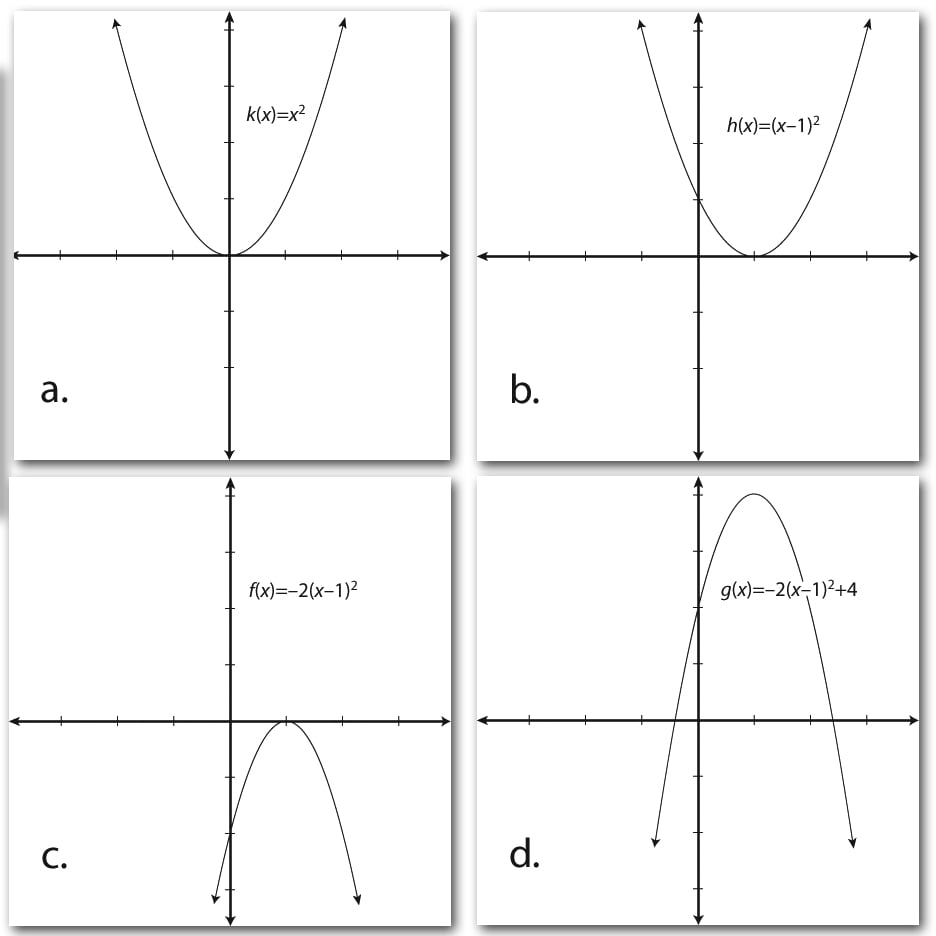



How To Combine Various Transformations Dummies




How To Graph Transformations Of Functions 14 Steps



Graphing With Transformations Quantitative Reasoning




Graph Transform Notes



1




Symmetry Transformations And Compositions
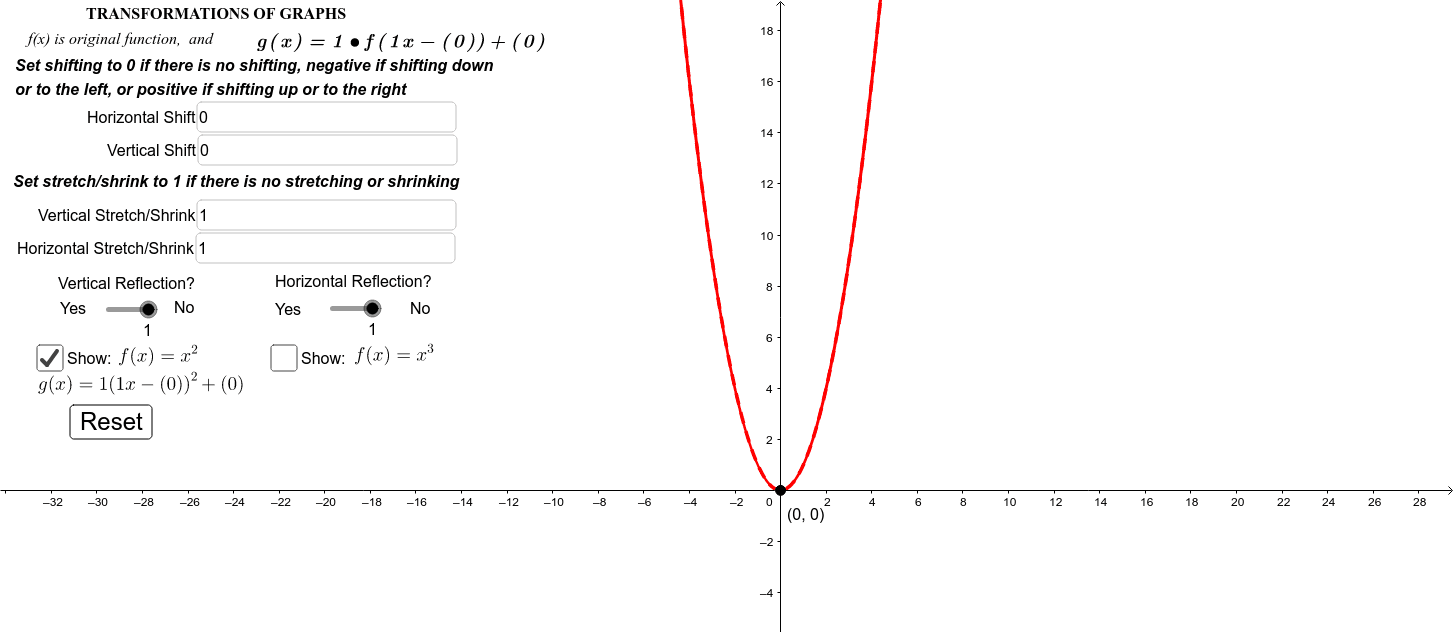



Transformation Of Y X 2 And Y X 3 Geogebra
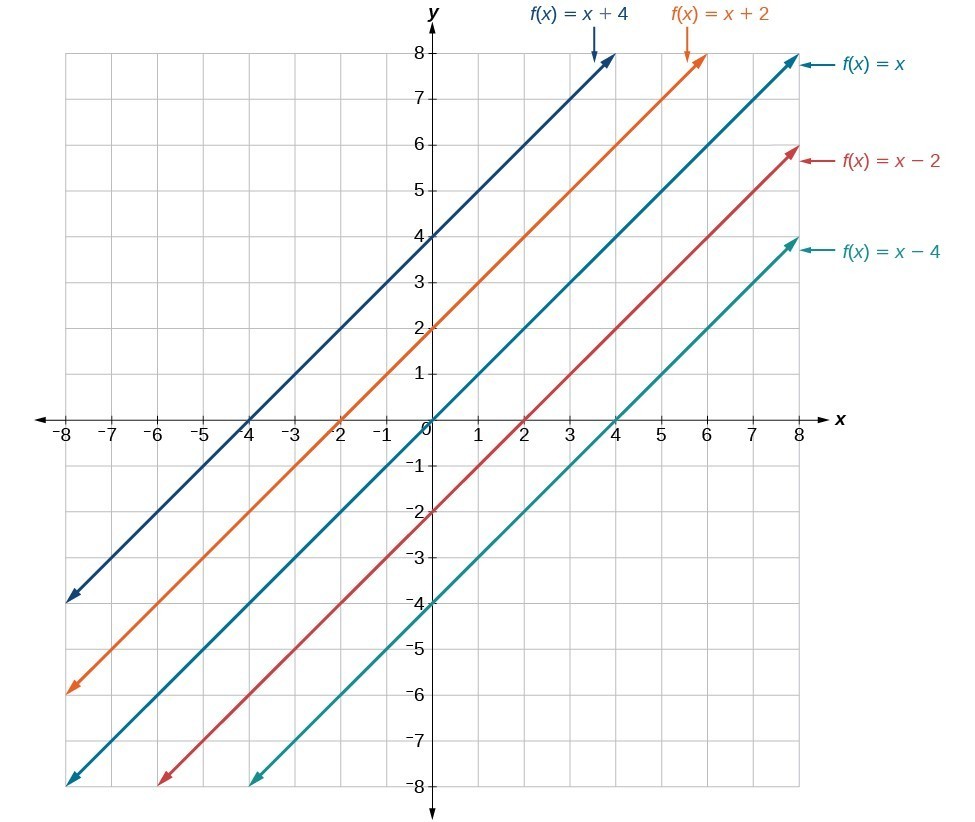



Read Transform Linear Functions Intermediate Algebra



Y X 2




Transformations Of Y X Ck 12 Foundation




Solved The Following Transformations Of Y X2 Results In Chegg Com
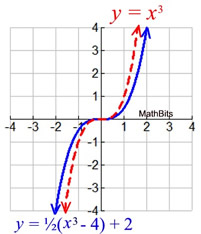



Sequence Of Transformations On Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math




Transformation Y X Geogebra
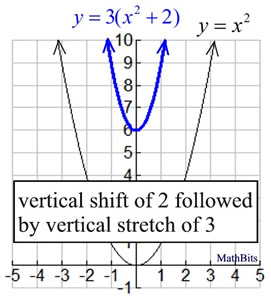



Sequence Of Transformations On Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math
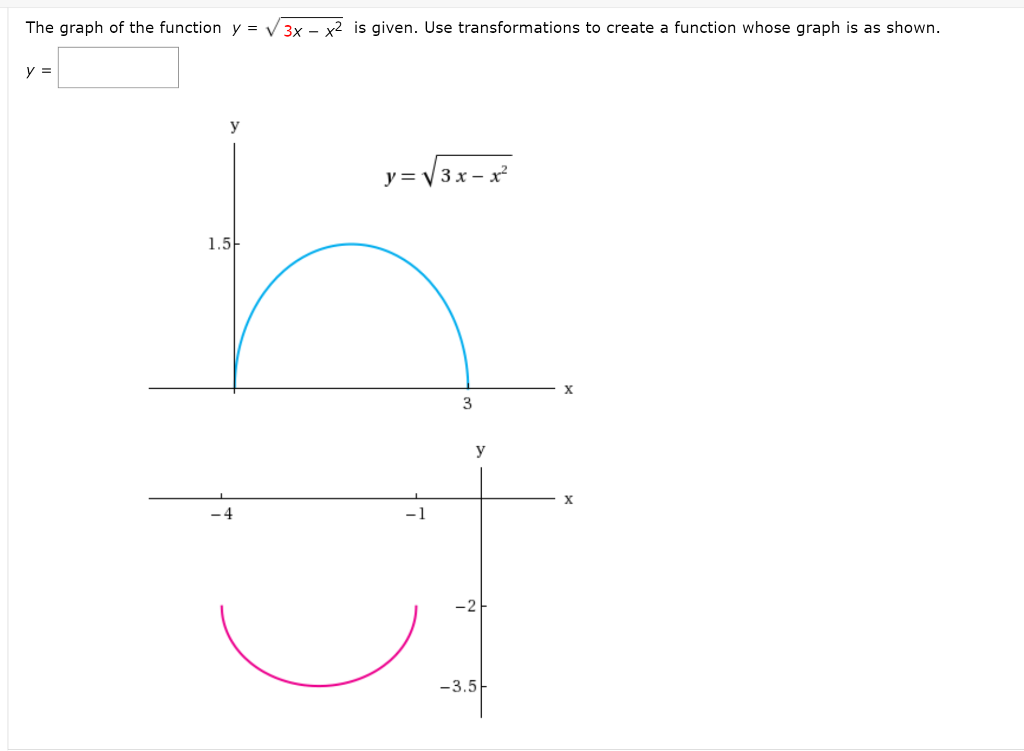



Solved The Graph Of The Function Y 3x X2 Is Given Use Chegg Com




Transformations Of Y X Ck 12 Foundation



1
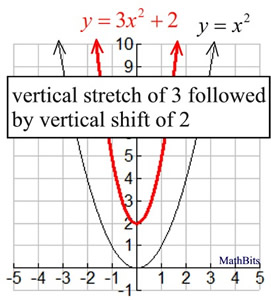



Sequence Of Transformations On Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math




Graph Transformations Mme
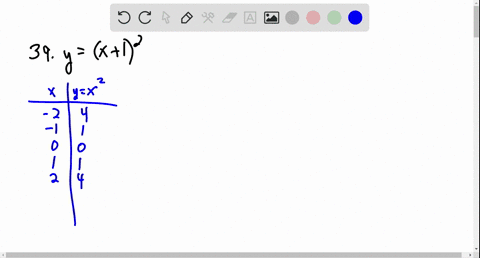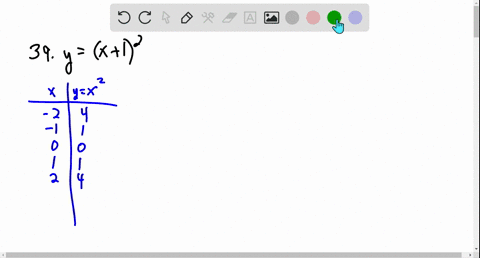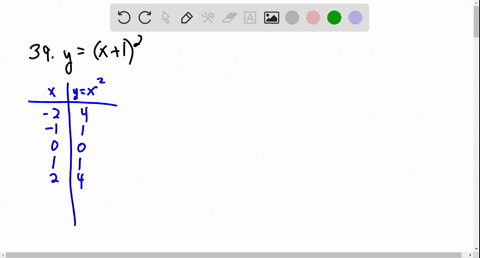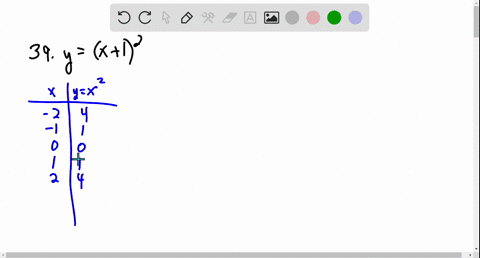



Solved Graph The Function Using Transformations Y X 2 3




14 More About Graphs Of Functions Transformation Effectively How To Memorise The Graphs Of Functions After O Y X A Translate The Graph Of Y F X K Ppt Download




Content Geometric Transformations Of Graphs Of Functions
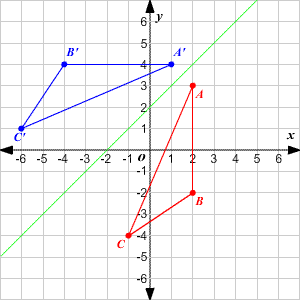



Transformations Of Graphs



What Transformations Are Needed To Transform The Graph Of The Parabola Y X 2 Into The Graph Of The Parabola Y X 2 4x 6 Quora




Graph The Function By Hand Not By Plotting Points But By Starting With The Gra Plainmath



Algebra 2 Transformations Of Parent Functions Youtube




This Graphical Representation Shows Transformations Associated With Y Download Scientific Diagram




Combining Transformations Ck 12 Foundation
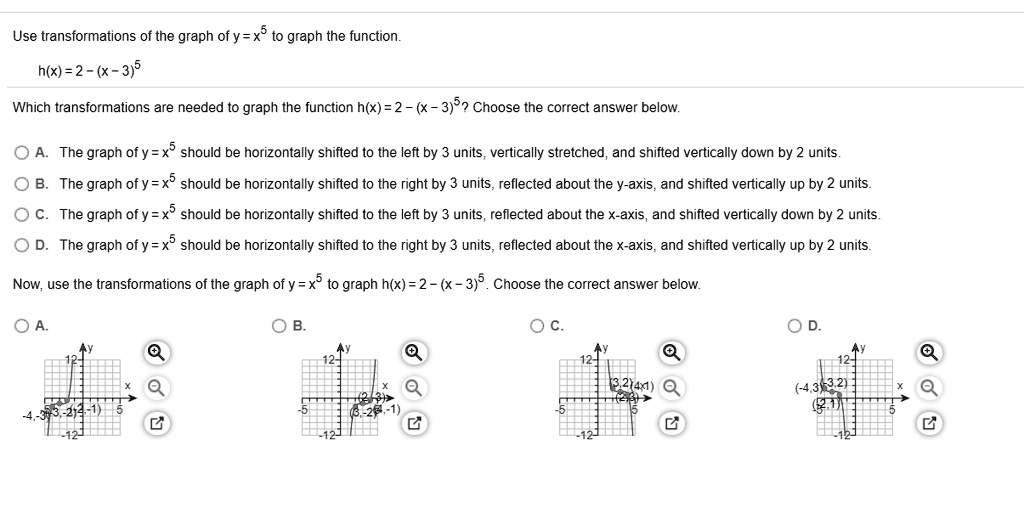



Solved Use Transformations Of The Graph Ofy X5 To Graph The Function H X 2 X 3 5 Which Transformations Are Needed T0 Graph The Function H X 2 X 3 52 Choose The Correct
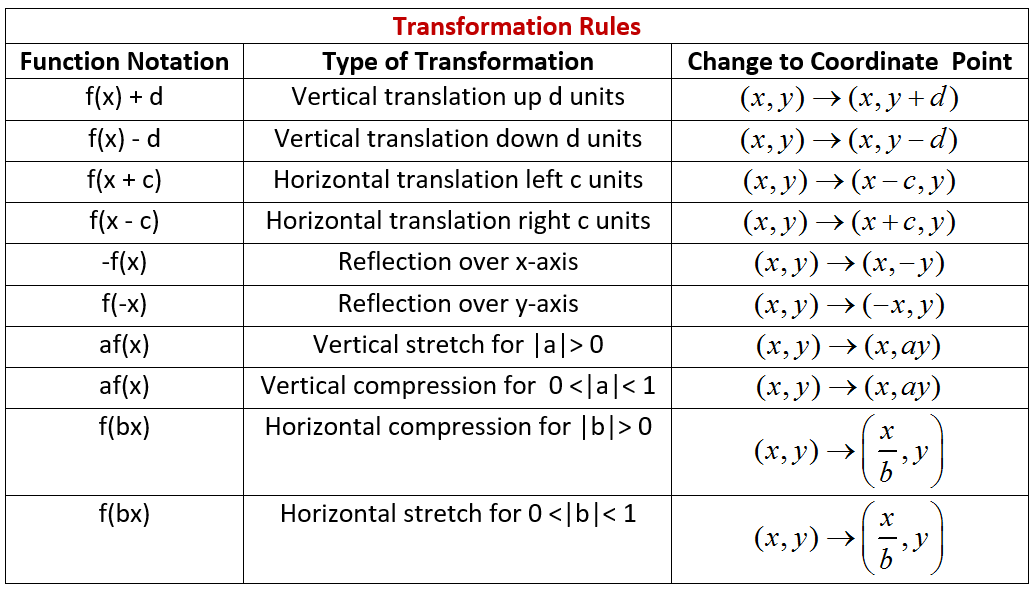



How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic



Trasformations By Graph Paper Teacher Guide
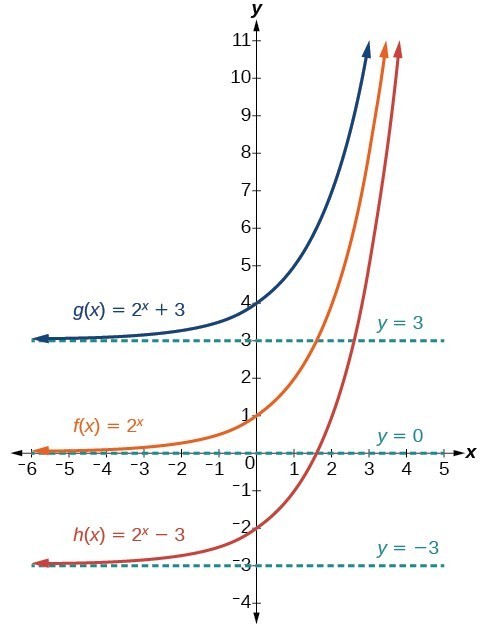



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿